Talk to Your SQL Server Database: Meet Copilot in SSMS 21
May 24, 2025Today, we will look at deploying Kubernetes AI Toolchain Operator (KAITO) straight from Visual Studio Code.
Last year, I wrote a blog article on Deploying Large Language Models on AKS with KAITO. Since then, the KAITO team has been working hard to make it easier to deploy and manage AI workloads on Kubernetes—and in this case, straight from Visual Studio Code using the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) extension.
So let’s look at how to deploy KAITO straight from Visual Studio Code.
I almost didn’t write this article due to the ease of deployment, but I noticed that a few people were searching for KAITO on my site, so I thought I would write it to help those who are looking for a way to deploy KAITO on AKS.
I have the following prerequisites already set up:
- An Azure account with an AKS cluster configured for KAITO, such as:
- Name:
KAITOcodetest - Location:
australiaeast - Kubernetes version:
1.31.7 - System pool: 2x
Standard_D8ds_v5(autoscaling 2-5, 300GB ephemeral OS disk, zone 1, taint:CriticalAddonsOnly=true:NoSchedule) - User pool: 2x
Standard_D8ds_v5(autoscaling 2-100, 300GB ephemeral OS disk, zone 1) - RBAC enabled, OIDC issuer enabled, Azure Policy and Container Insights enabled
- Network: Azure CNI Overlay, Standard Load Balancer
- Workload Identity enabled
- Name:
- Visual Studio Code installed
- The Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) extension is installed in Visual Studio Code
AKS Automatic clusters are not supported by the KAITO extension at this stage. You must use a standard AKS cluster.
So let’s get started. First, we need to install the KAITO workspace.
After authentication to Azure, we should be able to see the AKS cluster under your specific subscription. If you don’t see it, you may need to refresh the view or go and create the cluster first.
Let’s install the KAITO addon into the cluster first and set up the federated credentials— (this can take a few minutes to complete).
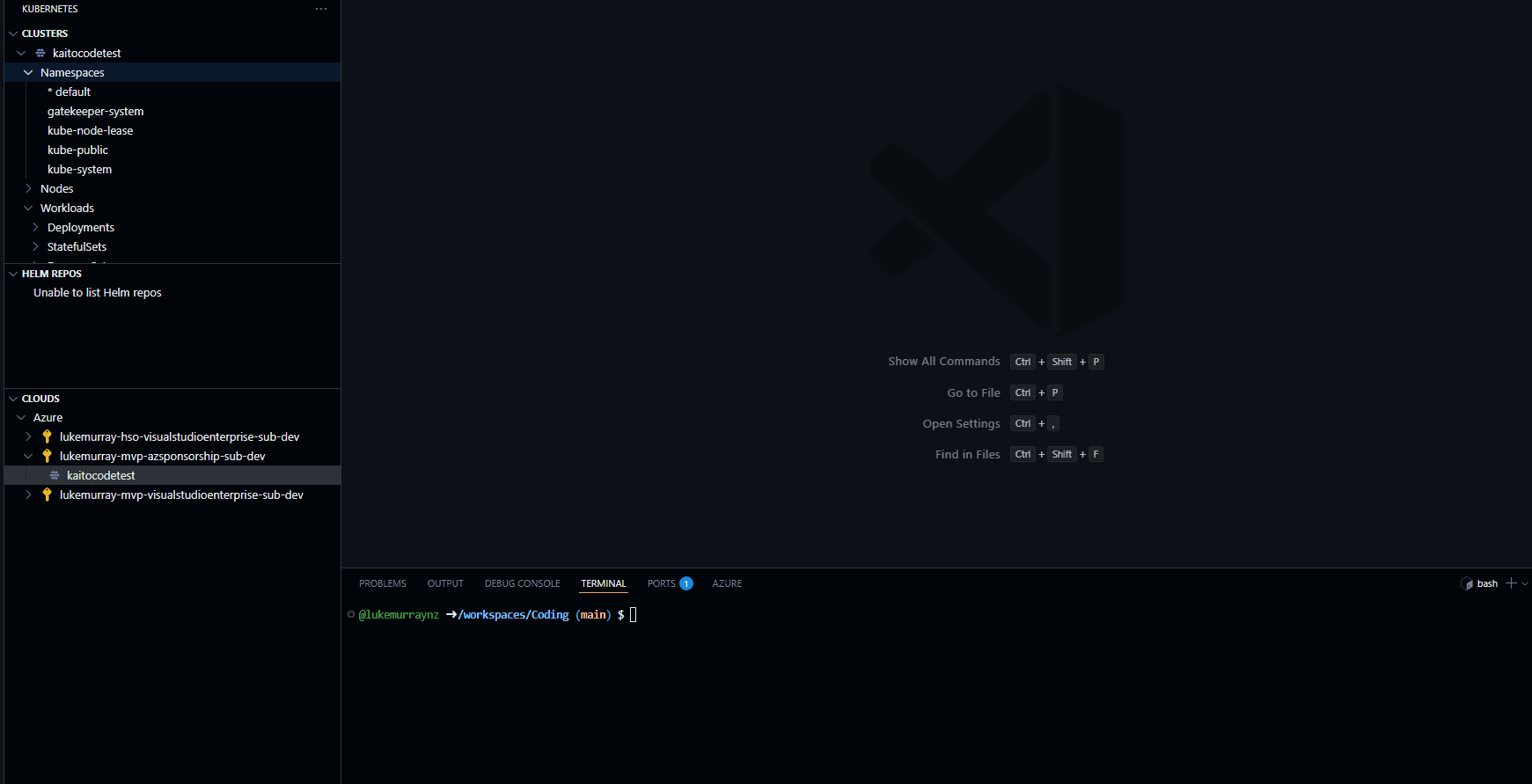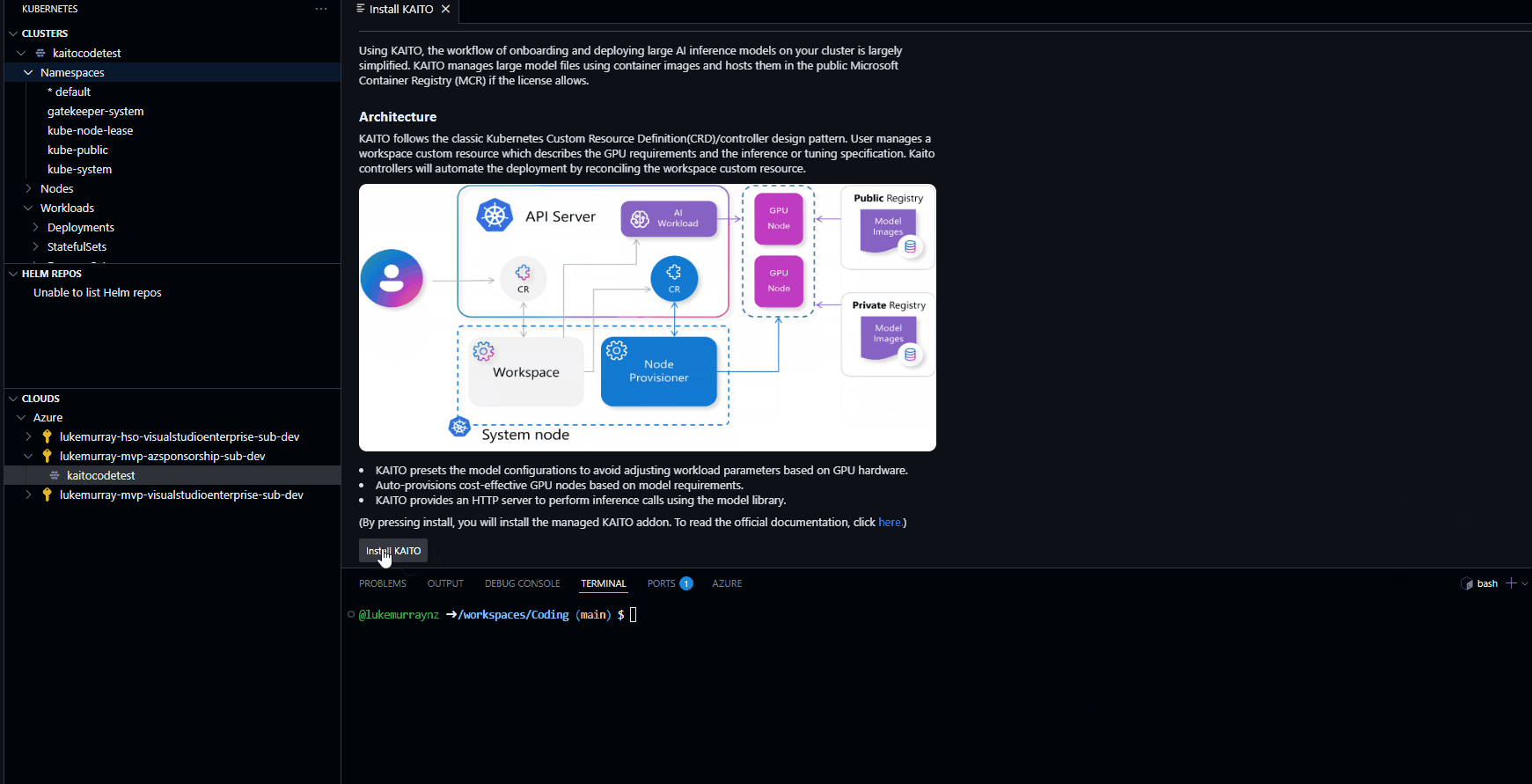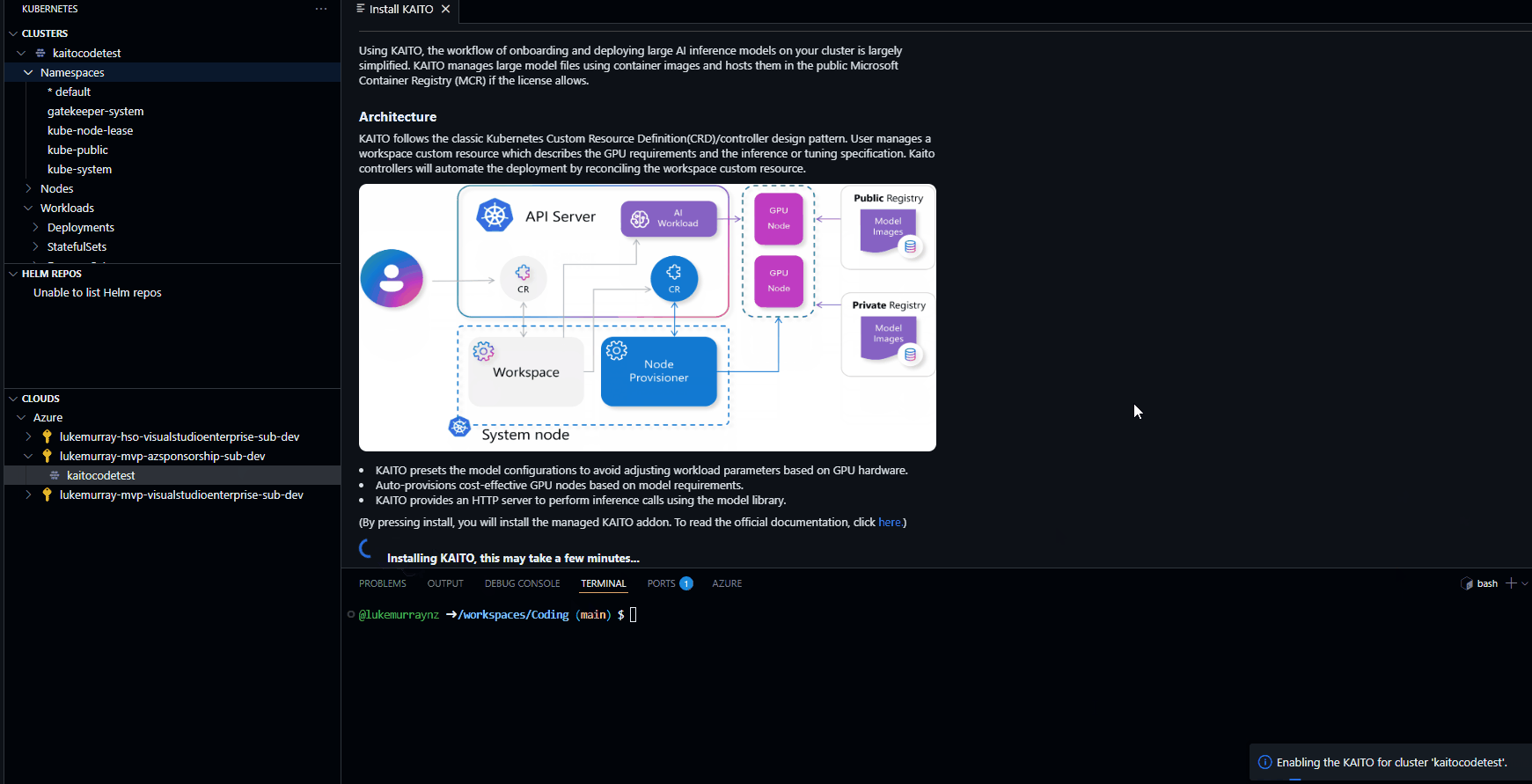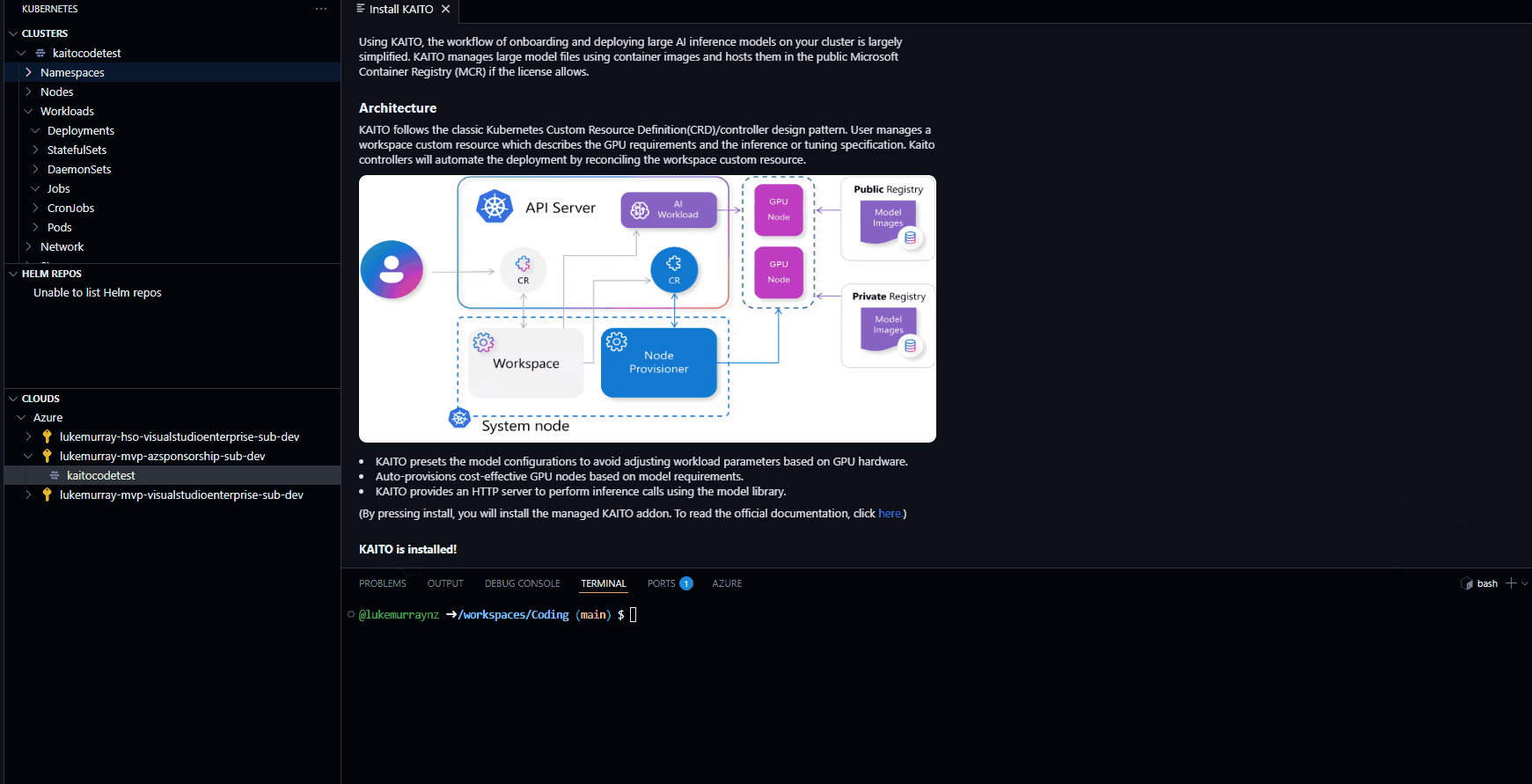
Once the KAITO addon is installed, we can create a new KAITO workspace. This will create a new namespace in the cluster and install the KAITO operator into that namespace.
As you can see, you can customise the CRD for the workspace, such as the name, VM compute, etc. In my case, I am going to use the base Standard_NC6s_v3 VM SKU, which is a 6 vCPU, 24GB RAM VM with 100GB ephemeral OS disk. This deployment can take 20-40 minutes or more to complete, so be patient.
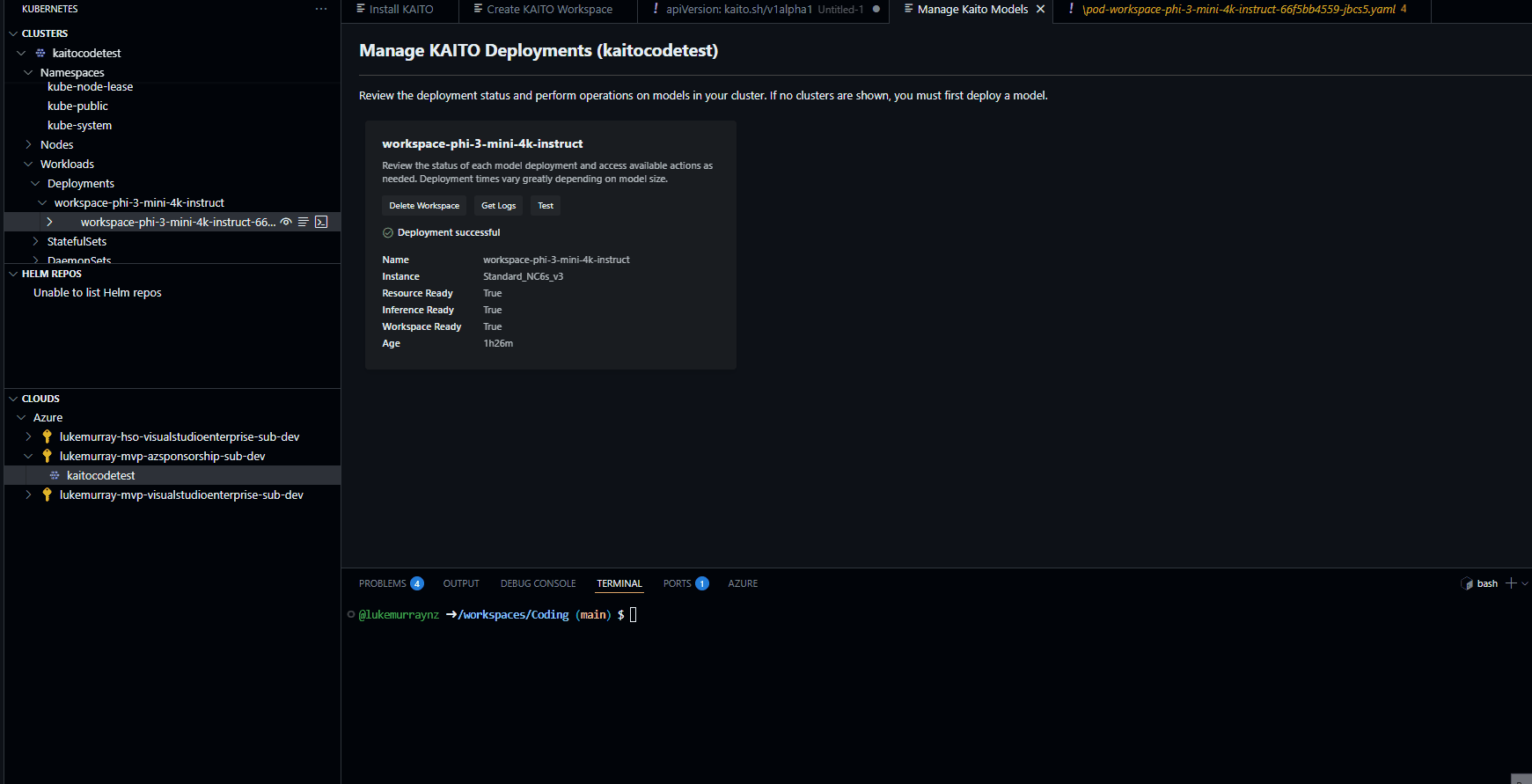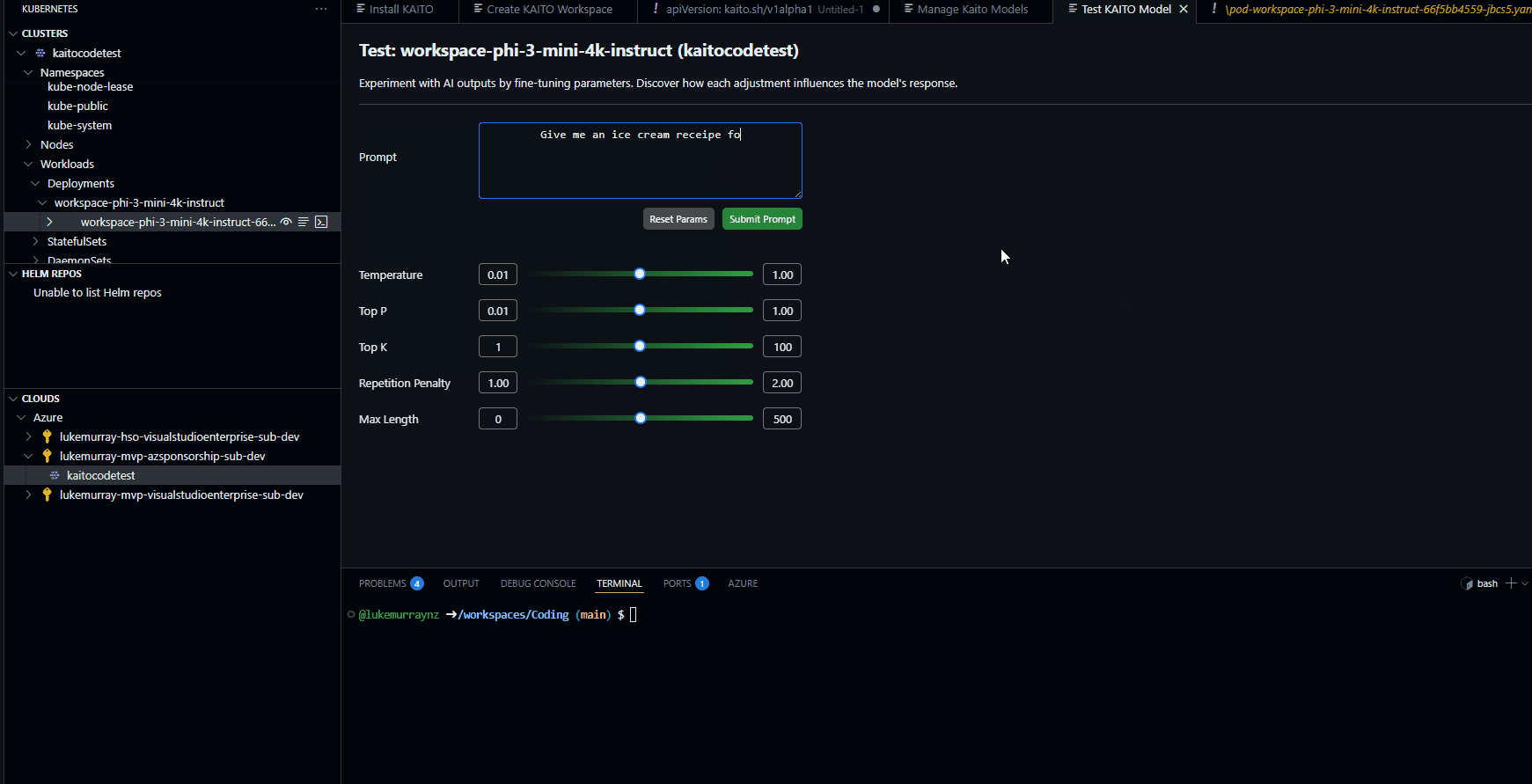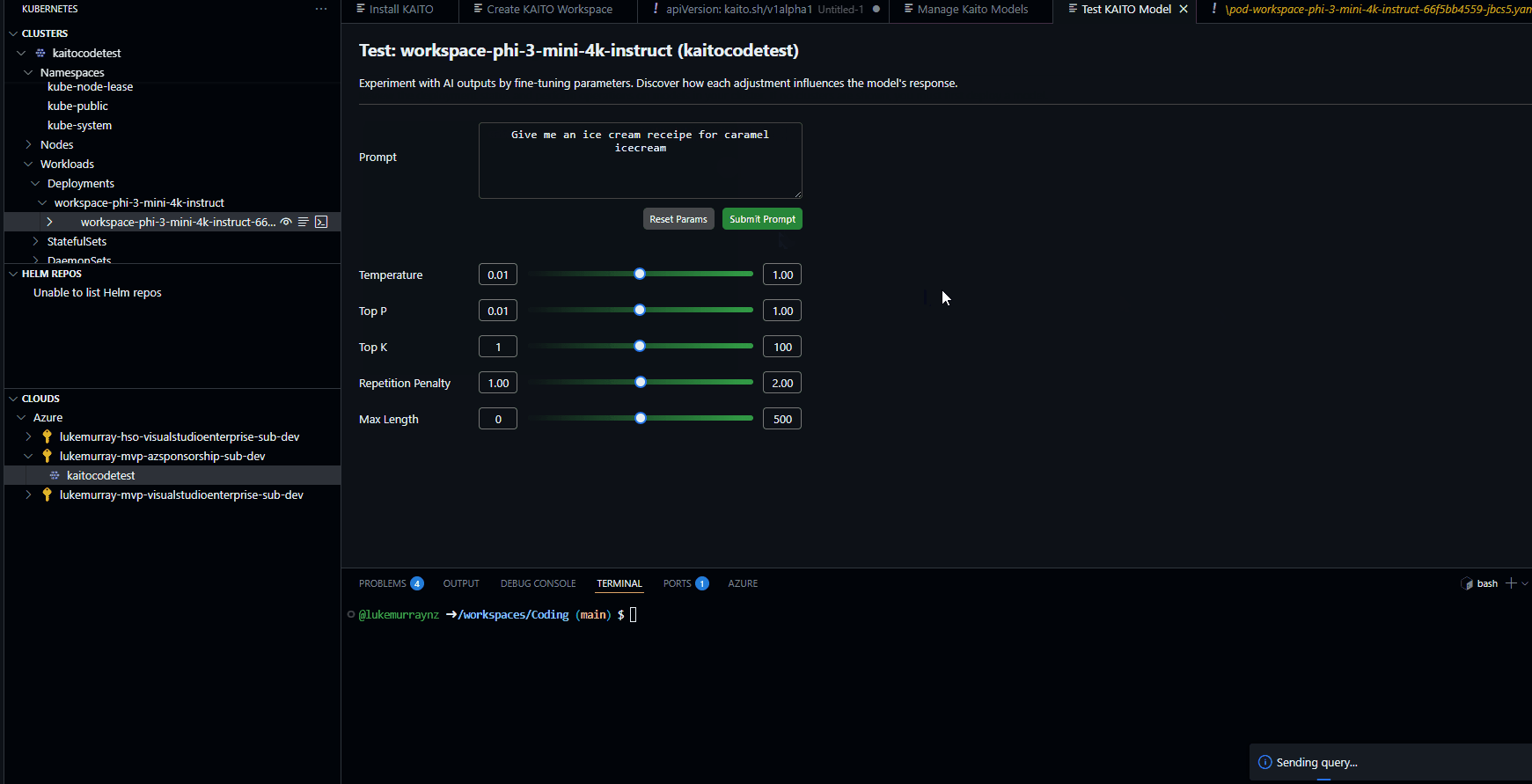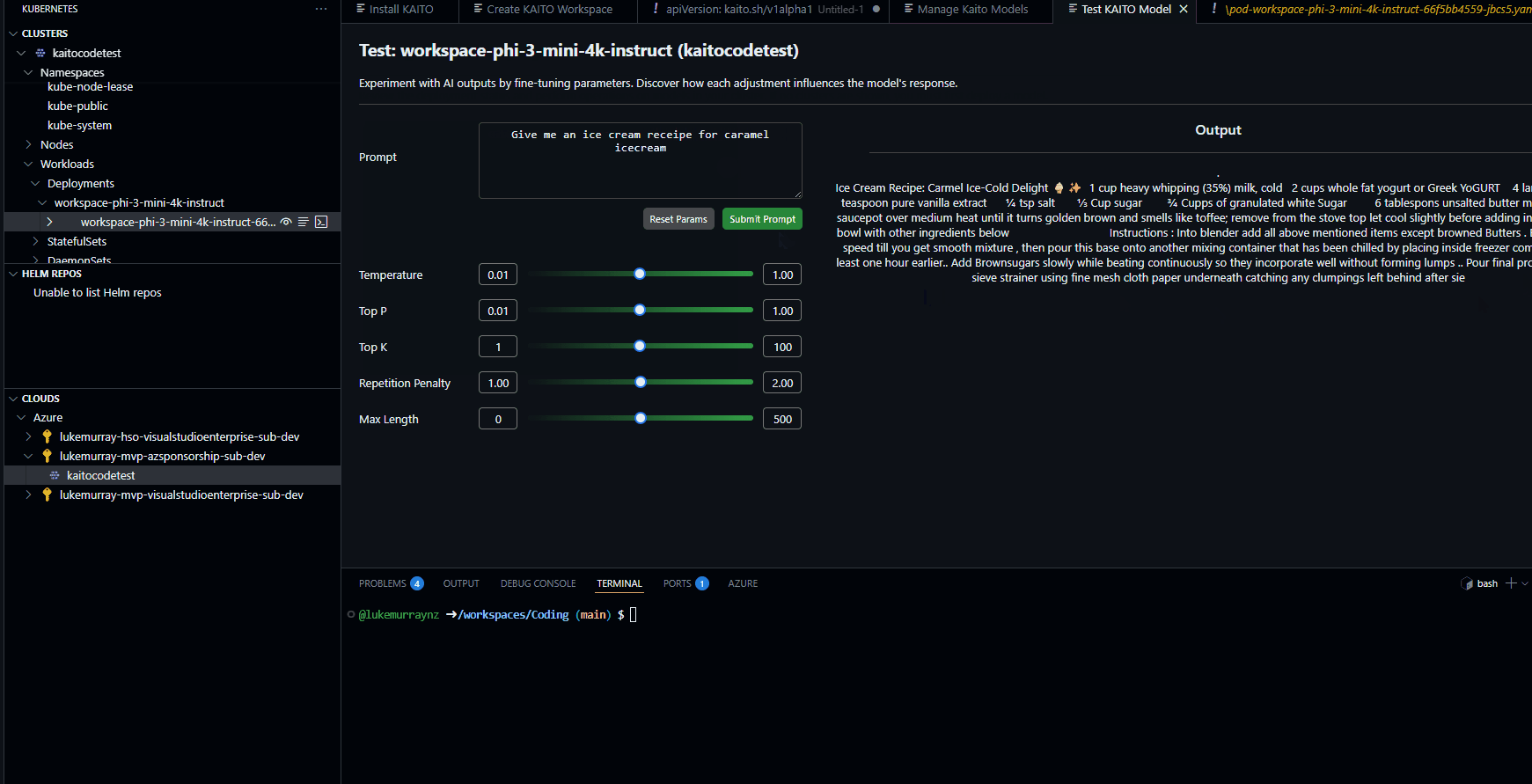
Once completed, you will see the deployment in the AKS extension view, and you can see the status of the workspace; in my example, it is running.
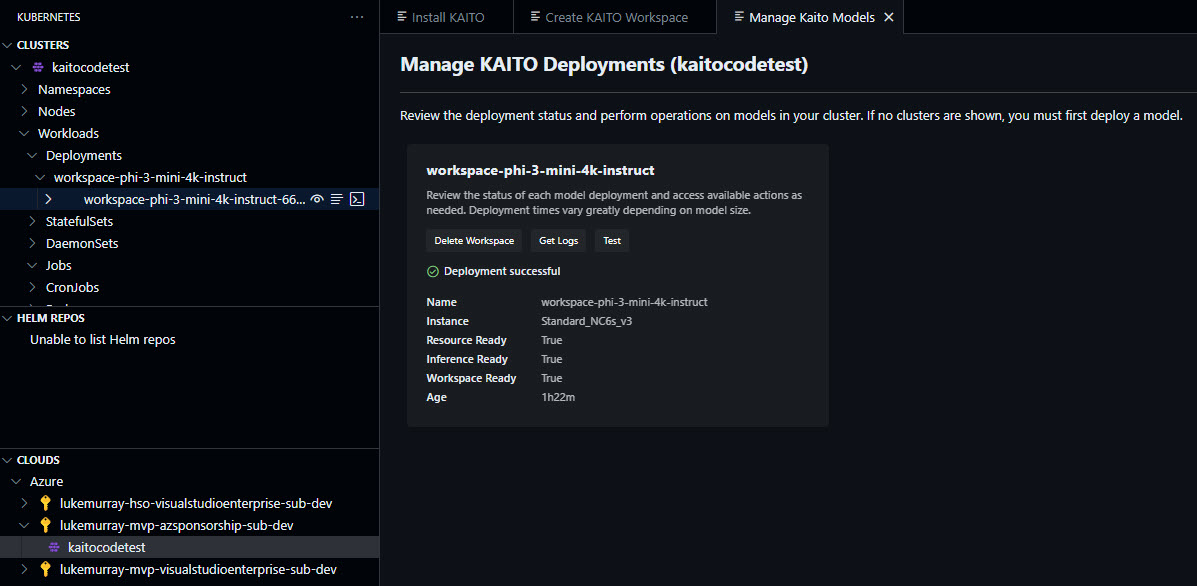
Now, let us test.